The Olea europaea, which is also known commonly as the olive tree, is widely cultivated in Mediterranean countries. Olive oil is the main product obtained from the olive tree and it’s highly respected for its organoleptic characteristics and for not leaving out its outstanding health benefits.
According to the International Olive Council (IOC), the first olive trees ever cultivated can be dated back to 6000 years in Asia Minor regions. The origin of the olive tree is linked to the Mediterranean civilization, with the region characterized by soft and rainy winters, hot-dry summers which all favor the cultivation of the olive tree (1).
Despite these climatic advantages to the Mediterranean region and also how large areas of land are required for the cultivation of the olive trees, its cultivation has rapidly spread to regions in almost all continents. However, the Mediterranean nations still hold the title as the main olive producers in the world and led by countries like Spain, Greece, and Italy. To affirm this claim, the European Union produces about 70% of the global olive production with a production value of about 7000 million euros each year (2).
Also, a famous French philosopher once wrote “There, where the olive tree gives up, is where the Mediterranean ends. The tree of light is the nature and culture of the Mediterranean.” This statement goes a long way to corroborate the development of a culture bound to olive-related products and of prime importance, the olive oil.
The Olive Oil
With the traditional and modern use of the oil, the olive oil is considered a staple food and is part of a cuisine known to be light, simple, and placid, with defined tastes full of harmony which is no other cuisine than the Mediterranean cuisine.
The olive oil comes with a wide variety of flavors, colors, and distinct features brought about by the differences in the vast array of olives from which the oil is extracted. The oil is resistant to the development of rancidity and blends perfectly in salad dishes.
Whether being used in salads or cooking, the exquisite taste of the oil is usually used alongside with herbs, spices and also complemented with the sharp taste of lemon, vinegar, or tomato. In deep frying, the oil shows a remarkable resistance due to its low unsaturated properties. This has made the oil not only recommended in salad dressing but for cooking and frying as well.
Production and Formulation of the Olive Oil
With vegetable oils, the production process can greatly affect the quality of the oil, the usage, stability and can even go a long way to determine the price of the oil. When it comes to buying or importing these oils, it is important to pay attention to the production process and how the production process can let one understand the quality or grade of the oil which can help in a better buying decision in accordance with the purpose or usage.
Types or grades of olive oils
There are basically three types or varieties of olive oils, which are; refined olive oil, virgin, and extra virgin. These oils vary in their various production processes and so is the quality of the oils obtained. Each oil has a different antioxidant activity, one of the main benefits of olive oil and other potential health benefits.
The antioxidant property of olive oil makes the oil very popular. Olive oil is considered one of the major food sources with high levels of antioxidants. Antioxidants protect the human body from damages and from harmful free radicals (3).
The unprocessed extra-virgin olive oil which is considered the best grade of the olive oil has the greatest antioxidant properties and highly recommended to consume raw especially in salad dressings.
The production of Olive Oil
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
Extra virgin olive oil as mentioned earlier is the top grade of olive oil available in the market. The process starts with harvesting, cleaning (separating the olives from leaves and branches), and washing of the olives to remove any foreign material that may cause issues with the machinery or contaminate the oil (4).
Once the olives are washed and cleaned, the olives are transported to the mills. Naturally, the olive fruit is made of approximately one-third of solid materials, water, and oil respectively. In the milling stage, which is the first true step of the production process, the objective is to crush the olives to produce a paste that facilitates the extraction of oil droplets.
The paste is then properly mixed in other to separate the oil from the pomace. This process is normally called malaxation. This process can greatly optimize the amount of oil obtained as a reduction in the oil-water emulsion is experienced. To obtain a cold-pressed oil, the temperature during the malaxation process is very important. The temperature is to be maintained below 27 degrees Celcius and above this temperature, the oil can’t be referred to as cold-pressed.
After the malaxation process, the oil can then be extracted by pressing, percolation, centrifugation, or better still through a combination of the different methods. To obtain the EVOO, the paste is actually spun instead of pressed even though extra virgin is still referred to as “first, cold-press.”
The EVOO can also be referred to as the olive fruit juice and it is typically poured in a glass and tasted like wine. This is because it’s the liquid extracted from the fruit of the olive. For the oil to be considered as EVOO, its acidity level must be lower than 0.8% and followed by other required parameters. This is the most expensive form of olive oil and should have no defects and characterize by a flavor of fresh olives (4b)
Virgin Olive Oil (VOO)
The same process the EVOO is obtained is the same way the VOO is processed. The only main difference is the acidity level after pressing which is seen at 2.0% max compared to the EVOO which must be below 0.8%. The main cause of the difference in acidity level for the EVOO and VOO is seen from either the olives themselves or the time period between harvest and production. As the olives can be exposed to more natural elements like sunlight, ripeness, or the time before harvest, contributes or affects the acidity level.
Since EVOO can be more pricey, producers can engage in producing the VOO to target or satisfy a certain customer base.
Refined Olive Oil
Refined oils are usually processed with high heat and are of low quality compared to other oils produced under low heat. Refined olive oil is practically virgin olive oil process under high heat for a more stable and mild light-tasting. Refined olive oil is characterized by a lower acidity level and fewer health benefits.
There exist other grades of oils from the olive fruit like the pure olive oil and the olive pomace oil;
Pure Olive Oil
Pure olive oil is a blend of refined olive oil and extra virgin olive oil or virgin olive oil and usually in any ratio. The oil is characterized by a milder taste and color compared to the other grades of olive oils
Olive Pomace Oil
Pomace is simply the pulp or the leftover squeezed olive paste after the extraction of extra virgin olive oil and virgin olive oil. To further obtain oil from the pomace, a chemical solvent is used called hexane (in most cases) to extract any remaining oil from the pomace. The chemical solvent is later removed from the extraction and the oil is refined to produce olive pomace oil.
Health benefits of olive oil
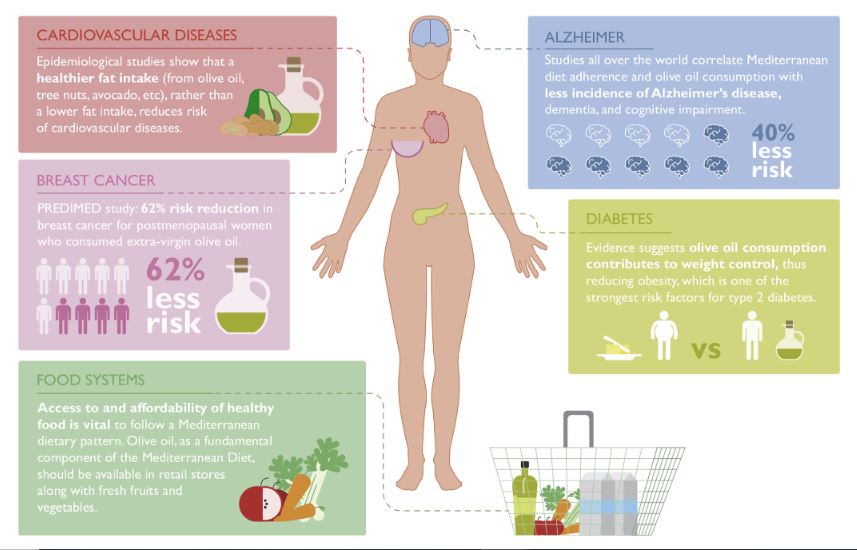
Our mission is to alter people’s eating habits around the world and to do that we strive to connect the world with the best healthy alternatives. It is important to point out some of the health benefits of olive oil for people to actually know what benefits they can get for an optimum health.
Olive oil has and is a major component in the Mediterranean diet for thousands of years dated back to the ancient Romans and Greek empires. Until this present moment, the oil remains the most popular cooking oil in the region. It is even believed the people of the Mediterranean region are healthier and tend to live longer due to their diet which is highly rich in olive oils and unprocessed plant foods. (5).
The olive oil is packed with antioxidants as mentioned earlier and monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) which are highly considered as healthy fats by experts (6). Below are some of the health benefits of olive oil;
1)- The huge amount of antioxidants present in the oil.
Antioxidants are actively known to fight against and protect the body from free radicals and cellular damage that may lead to a series of health complications. Extra virgin olive oil contains the highest amount of antioxidants because of the way the oil is processed.
These antioxidants are known to be biologically active and may help with chronic health complications(7) (8). Also, they may help reduce inflammation and protects the blood cholesterols from oxidation, and in return mitigate the risk of heart disease (9)(10).
2)- The presence of high amounts of monounsaturated fats (MUFAs)
Even though olive oil contains about 14% saturated fat and over 11% polyunsaturated fats (omega-6 and omega-3), the oil also contains 73% of a predominant monounsaturated fatty acid known as oleic acid. Oleic acid is best known to reduce inflammation and also beneficial to cancer-related genes (11)(12)
3)- Olive oil strengthens cardiovascular health
Olive oil is well known to be good for a healthy heart and some studies have been able to validate this fact. A study was able to demonstrate that, eating a Mediterranean-style diet that comprises over 4 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil in a day face less risk of developing heart-related complications, and the chances of a heart attack, or stroke was 30% less than people who consume a low-fat diet (13).
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) also recommends a 1½ tablespoon of oleic-rich oils like olive oil can help reduce the risk of coronary heart disease (14).
4)- High in polyphenols
Olive oils are known to be a rich source of polyphenols and particularly extra virgin olive oil. Polyphenols are simply micronutrients that are naturally present in plants. We can easily obtain polyphenols in our diet when we consume foods like fruits, teas, vegetables, and spices (15). Polyphenols are well known to manage blood pressure levels and maintain healthy and flexible blood vessels.
Polyphenols can also help to limit oxidative stress which may lead to or cause heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and dementia. The polyphenols present in olive oil are known to be oleocanthal and hydroxytyrosol. These polyphenols are high in antioxidants, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties.
5)- Olive oil can help with type 2 diabetes
Extra virgin olive oil is well known to lower or moderate blood glucose and cholesterol levels (16). Compared to other kinds of fats, extra virgin olive oil reduces blood sugar and cholesterol levels more than any other.
Numerous studies have been able to demonstrate the beneficial effects of olive oil on blood sugar and insulin sensitivity (17)(18). In a random research, over 418 participants were able to confirm how a Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes by about 40% (19).
Other health benefits of olive oil may include;
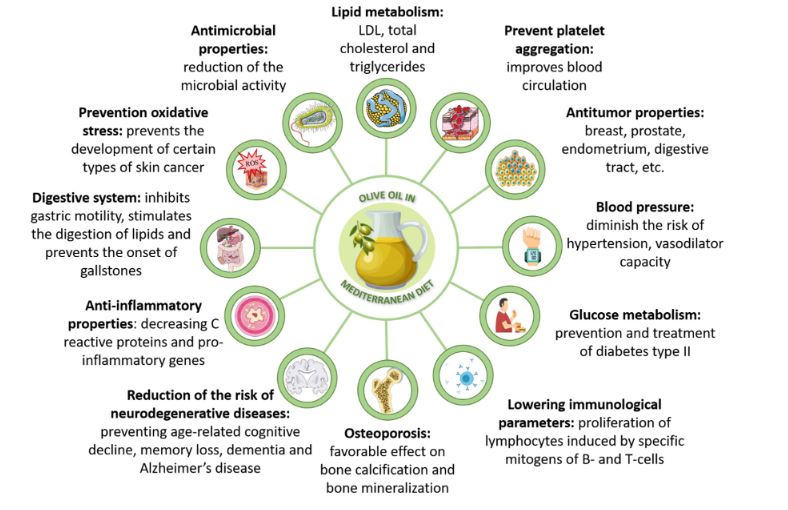
- Olive oil contains strong anti-inflammatory properties (20)(21)(22).
- Olive oil may help to prevent strokes (23) (24).
- Weight gain and obesity are not associated with olive oil. (23) (24) (25).
- Olive oil may help to fight against Alzheimer’s disease (26) (27).
- It is known to have anti-cancer benefits (28) (29).
- Rheumatoid Arthritis can be prevented with the help of olive oil (30) (31) (32).
- Olive oil is known to have antibacterial properties (33) (34)
- It supports and strengthens the immune system (35)
- The oil can help support a healthy gut microbiome (36)
- Olive oil can help boost bone health (37) (38)
Top 10 Exporters of Olive Oils in the World as of 2020
| Exporters | Value exported in 2020 (USD thousand) | Trade balance in 2020 (USD thousand) | Quantity exported in 2020 | Quantity Unit | Share in world exports (%) |
| Spain | 3,214,614 | 2,670,567 | 1,121,200 | Tons | 42.3 |
| Italy | 1,604,327 | 84,402 | 373,271 | Tons | 21.1 |
| Tunisia | 882,659 | 881,792 | 364,582 | Tons | 11.6 |
| Portugal | 639,016 | 295,177 | 197,543 | Tons | 8.4 |
| Greece | 562,487 | 557,142 | 174,461 | Tons | 7.4 |
| Turkey | 129,296 | 58,477 | 53,697 | Tons | 1.7 |
| Syrian Arab Republic | 103,918 | 100,941 | 55,958 | Tons | 1.4 |
| France | 61,645 | -431,789 | 9,789 | Tons | 0.8 |
| Argentina | 60,753 | 58,557 | 22,177 | Tons | 0.8 |
| Chile | 57,179 | 52,062 | 21,296 | Tons | 0.8 |
Which country is the largest exporter of olive oil?
As of 2020, Spain is the biggest exporter of olive oil in the world with a market share of 42.3% and exporting over 1.1 million tons of olive oil to the world with an export value of about $3.214 trillion USD. At second spot comes Italy with an export value of $1.6 trillion USD for an export of over 373,271 tons of olive oil with a market share of 21.1%. Tunisia can be spotted at the third spot with a market share of 11.6% exporting over 364,582 tons of olive oil with a market value of over $881.7 million USD. All three countries combined, control a market share of 75%.
Import considerations for olive oil
It is very important to always research on the import requirements for any product if you are looking to import for the first time. Countries have their laws towards importing certain products and how they are being categorized. With such information, you can conveniently understand how to meet the requirement for importing the product into your market or market.
An example, with importing olive oils in the US market, Olive oil falls into some categories which largely depends on the end use of the oil. If the oil is imported as food or for cooking, the shipment needs to be in compliance with the laws of FDA. In this case the shipment is required to have;
- – A food facility registration
- – Country of Origin ( Must be an area or region which is FDA approved).
- – Prior notice of imported food
- – Foreign Supplier Verification Programs (FSVP)
- – Clears CBP (Customs Border Protection)
Also, FDA requires foods to meet the same standards as foods produced within the United States. If any requirement is neglected during the import process, the shipment can be delayed or worst still, returned.
Another important consideration is to make sure you get the right type of oil. Importing the right type of olive oil can be really important or better still what does the market need. A market research can be important at this point. Extra virgin olive oil is the most sort after since it is the best quality health-wise.
Also, one should be mindful of the ongoing fraud in the olive oil space. Blended oils or olive oils diluted with other refined oils are labeled as “extra virgin.” It is important to check properly and make sure you are getting the correct grade of olive oil.
Everything now falls to sourcing the right supplier. You must look at the reputation of the company, what standards do they stand for? What’s the quality of the oils they produce? What’s their consistency level? and also you must look into their production process.
The price point is also very important and you need to know what your market is willing to pay for the olive oil you are looking to import. Don’t be carried away by illegitimate companies offering lower prices as olive oil is an expensive oil. It is very important to understand why the oil is priced the way it is to avoid being scammed.
Also, it is very important to consider the packing requirements, shipping conditions, and labeling. In certain markets, the labeling must cover certain information before it can be accepted. When it comes to packaging and bottling, olive oil should not be filled or bottled in clear glass bottles as light is an enemy to olive oil. Olive oil is usually filled in dark green bottles to help protect the oil from UV light which may cause the oil to deteriorate.




